1.Globalization(Application that function for multiple cultures- Using unicode, Formatting date, number and currencies calender) vs localization(cluture translation text , adapting UI elements and Adjusting image and icons)
Saturday, 29 March 2025
10+ Years Question and answers
Thursday, 20 March 2025
10+ Years .NET Interview Questions and answers
1. Sql profiler - performance tracking
- Singleton design
- Dispose and finally
- Boxing and unboxing
- Unmanaged vs managed code
- Early and lazy binding
- Entity framework
- Dependency injection in .net core
- Inbuilt container for DI
- .net core VS .net classic
- Nuget package usage
- Startup.cs what is used
- Use of program.cs
- Service registration in startup.cs
- www.root folder
- App.setting.json
- Session and state management in .net core
- Rest in webapi
- SOAP vs Rest
- Token based authentication
- SQL - SQL Profile
Friday, 28 February 2025
List Remove VS RemoveAt
List Remove - will remove the value from the list
List RemoveAt - will remove the index value
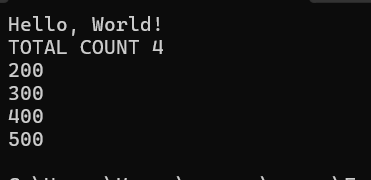
List Remove
List<int> intsList = new List<int>();
intsList.Add(100);
intsList.Add(200);
intsList.Add(300);
intsList.Add(400);
intsList.Add(500);
intsList.Remove(1);
Console.WriteLine("TOTAL COUNT "+intsList.Count);
foreach (int i in intsList)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
OUTPUT:
ArrayList Remove VS RemoveAt Example
ArrayList with RemoveAt
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.Add("1");
arrayList.Add("2");
arrayList.Add("3");
arrayList.Add("4");
arrayList.Add("5");
arrayList.RemoveAt(2);
Console.WriteLine(arrayList.Count);
OUTPUT:
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.Add("1");
arrayList.Add("2");
arrayList.Add("3");
arrayList.Add("4");
arrayList.Add("5");
arrayList.Remove("2");
Console.WriteLine("TOtal count: "+arrayList.Count);
foreach (string i in arrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
OUTPUT:
Monday, 24 February 2025
Web API Vs REST API
| Web API type | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| REST | Follows REST architecture | RESTful |
| SOAP | Utilizes XML, strict standards | Non-RESTful |
| GraphQL | Flexible query language | Non-RESTful |
|
Web
API |
REST
API |
|
|
What
they are |
Web
APIs encompass any API using HTTP or HTTPS. All REST APIs are Web APIs, but
not all Web APIs are RESTful. |
REST
APIs are Web APIs that follow specific architectural principles like
statelessness and client-server architecture. |
|
State |
Technically,
they can be stateless or stateful. |
Statelessness
implies that between sessions of API invocation, the server that hosts the
program doesn’t need to ‘remember’ or hold any information between sessions
to perform the appropriate action. |
|
When to
choose |
Non-RESTful
Web APIs are used for stateful operations, ACID-compliant transactions with a
web server, and working with legacy systems. |
Statelessness
is the main consideration when choosing RESTful APIs over non-RESTful APIs. |
|
Common
use case |
Many
legacy systems, especially those that communicate with systems such as
hardware or IoT devices, also use non-REST-based APIs. |
RESTful
APIs are often used in web services that require standardized communication
and interoperability between different systems. |
Sort the Array without inbuild function
Sorting by ascending order
int[] Arrayorder = {3,7,4,1,2,9,8 };
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < Arrayorder.Length-1; i++)
{
for (int j = i+1; j < Arrayorder.Length; j++)
{
if (Arrayorder[i] > Arrayorder[j])
{
temp = Arrayorder[i];
Arrayorder[i] = Arrayorder[j];
Arrayorder[j] = temp;
}
}
}
foreach (int i in Arrayorder)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Output:
Sorting by Descending order
int[] Arrayorder = {3,7,4,1,2,9,8 };
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < Arrayorder.Length-1; i++)
{
for (int j = i+1; j < Arrayorder.Length; j++)
{
if (Arrayorder[i] < Arrayorder[j])
{
temp = Arrayorder[i];
Arrayorder[i] = Arrayorder[j];
Arrayorder[j] = temp;
}
}
}
foreach (int i in Arrayorder)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Output:
Saturday, 22 February 2025
Delegates SingleCast & MultiCast
In C#, there are two kinds of Delegates. These are:
SingleCast Delegate: A single function or method is referred to as a delegate.
// Using of Delegates
using System;
class Geeks
{
// Declaring the delegates
// Here return type and parameter type should
// be same as the return type and parameter type
// of the two methods
// "addnum" and "subnum" are two delegate names
public delegate void addnum(int a, int b);
public delegate void subnum(int a, int b);
public void sum(int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine("(100 + 40) = {0}", a + b);
}
public void subtract(int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine("(100 - 60) = {0}", a - b);
}
// Main Method
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// creating object "obj" of class "Geeks"
Geeks obj = new Geeks();
// creating object of delegate, name as "del_obj1"
// for method "sum" and "del_obj2" for method "subtract" &
// pass the parameter as the two methods by class object "obj"
// instantiating the delegates
addnum del_obj1 = new addnum(obj.sum);
subnum del_obj2 = new subnum(obj.subtract);
// pass the values to the methods by delegate object
del_obj1(100, 40);
del_obj2(100, 60);
// These can be written as using
// "Invoke" method
// del_obj1.Invoke(100, 40);
// del_obj2.Invoke(100, 60);
}
}
MultiCast Delegate: Delegate refers to the delegation of multiple functions or methods.
// C# program to illustrate the
// Multicasting of Delegates
using System;
class rectangle {
// declaring delegate
public delegate void rectDelegate(double height,
double width);
// "area" method
public void area(double height, double width)
{
Console.WriteLine("Area is: {0}", (width * height));
}
// "perimeter" method
public void perimeter(double height, double width)
{
Console.WriteLine("Perimeter is: {0} ", 2 * (width + height));
}
// Main Method
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// creating object of class
// "rectangle", named as "rect"
rectangle rect = new rectangle();
// these two lines are normal calling
// of that two methods
// rect.area(6.3, 4.2);
// rect.perimeter(6.3, 4.2);
// creating delegate object, name as "rectdele"
// and pass the method as parameter by
// class object "rect"
rectDelegate rectdele = new rectDelegate(rect.area);
// also can be written as
// rectDelegate rectdele = rect.area;
// call 2nd method "perimeter"
// Multicasting
rectdele += rect.perimeter;
// pass the values in two method
// by using "Invoke" method
rectdele.Invoke(6.3, 4.2);
Console.WriteLine();
// call the methods with
// different values
rectdele.Invoke(16.3, 10.3);
}
}
Clean architecture VS Onion architecture
Terminology:
Clean Architecture: Uses terms like "Entities" (domain model), "Use Cases" (application logic), "Interface Adapters" (connecting to external frameworks), and "Frameworks & Drivers" (UI, database).
Onion Architecture: Focuses on layers like "Domain" (core business logic), "Application" (coordinates interactions), "Infrastructure" (database access, external services).
Application Layer Focus:
Clean Architecture: The "Use Cases" layer is central to the application logic, defining the primary business operations that can be easily tested in isolation.
Inner layer is not depend on the outer layer but outer layer are depend on the inner layer
Onion Architecture: The "Application" layer acts as a coordinator between the Domain and Infrastructure layers, with less emphasis on specific "Use Cases" terminology.
Parallel Threading
Parallelize operations by using Invoke in the Task Parallel Library. Three operations are performed on a shared data source. The operations can be executed in parallel in a straightforward manner, because none of them modifies the source.
namespace ParallelTasks
{
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Net;
class ParallelInvoke
{
static void Main()
{
// Retrieve Goncharov's "Oblomov" from Gutenberg.org.
string[] words = CreateWordArray(@"http://www.gutenberg.org/files/54700/54700-0.txt");
#region ParallelTasks
// Perform three tasks in parallel on the source array
Parallel.Invoke(
() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Begin first task...");
GetLongestWord(words);
}, // close first Action
() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Begin second task...");
GetMostCommonWords(words);
}, //close second Action
() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Begin third task...");
GetCountForWord(words, "sleep");
} //close third Action
); //close parallel.invoke
Console.WriteLine("Returned from Parallel.Invoke");
#endregion
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit");
Console.ReadKey();
}
#region HelperMethods
private static void GetCountForWord(string[] words, string term)
{
var findWord = from word in words
where word.ToUpper().Contains(term.ToUpper())
select word;
Console.WriteLine($@"Task 3 -- The word ""{term}"" occurs {findWord.Count()} times.");
}
private static void GetMostCommonWords(string[] words)
{
var frequencyOrder = from word in words
where word.Length > 6
group word by word into g
orderby g.Count() descending
select g.Key;
var commonWords = frequencyOrder.Take(10);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.AppendLine("Task 2 -- The most common words are:");
foreach (var v in commonWords)
{
sb.AppendLine(" " + v);
}
Console.WriteLine(sb.ToString());
}
private static string GetLongestWord(string[] words)
{
var longestWord = (from w in words
orderby w.Length descending
select w).First();
Console.WriteLine($"Task 1 -- The longest word is {longestWord}.");
return longestWord;
}
// An http request performed synchronously for simplicity.
static string[] CreateWordArray(string uri)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Retrieving from {uri}");
// Download a web page the easy way.
string s = new WebClient().DownloadString(uri);
// Separate string into an array of words, removing some common punctuation.
return s.Split(
new char[] { ' ', '\u000A', ',', '.', ';', ':', '-', '_', '/' },
StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
}
#endregion
}
}
// The example displays output like the following:
// Retrieving from http://www.gutenberg.org/files/54700/54700-0.txt
// Begin first task...
// Begin second task...
// Begin third task...
// Task 2 -- The most common words are:
// Oblomov
// himself
// Schtoltz
// Gutenberg
// Project
// another
// thought
// Oblomov's
// nothing
// replied
//
// Task 1 -- The longest word is incomprehensible.
// Task 3 -- The word "sleep" occurs 57 times.
// Returned from Parallel.Invoke
// Press any key to exit
Saturday, 4 January 2025
SQL Query for find manager with in the same name
Table
Query
select e.Emp_Name,m.Emp_Name as Manager from EmpDetails e
left join EmpDetails m on m.Manager_Id=e.id