1.Globalization(Application that function for multiple cultures- Using unicode, Formatting date, number and currencies calender) vs localization(cluture translation text , adapting UI elements and Adjusting image and icons)
.Net , SQL & React
Saturday, 29 March 2025
10+ Years Question and answers
Thursday, 20 March 2025
10+ Years .NET Interview Questions and answers
1. Sql profiler - performance tracking
- Singleton design
- Dispose and finally
- Boxing and unboxing
- Unmanaged vs managed code
- Early and lazy binding
- Entity framework
- Dependency injection in .net core
- Inbuilt container for DI
- .net core VS .net classic
- Nuget package usage
- Startup.cs what is used
- Use of program.cs
- Service registration in startup.cs
- www.root folder
- App.setting.json
- Session and state management in .net core
- Rest in webapi
- SOAP vs Rest
- Token based authentication
- SQL - SQL Profile
Friday, 28 February 2025
List Remove VS RemoveAt
List Remove - will remove the value from the list
List RemoveAt - will remove the index value
List Remove
List<int> intsList = new List<int>();
intsList.Add(100);
intsList.Add(200);
intsList.Add(300);
intsList.Add(400);
intsList.Add(500);
intsList.Remove(1);
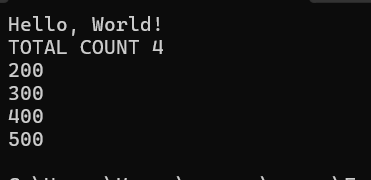
Console.WriteLine("TOTAL COUNT "+intsList.Count);
foreach (int i in intsList)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
OUTPUT:
ArrayList Remove VS RemoveAt Example
ArrayList with RemoveAt
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.Add("1");
arrayList.Add("2");
arrayList.Add("3");
arrayList.Add("4");
arrayList.Add("5");
arrayList.RemoveAt(2);
Console.WriteLine(arrayList.Count);
OUTPUT:
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
arrayList.Add("1");
arrayList.Add("2");
arrayList.Add("3");
arrayList.Add("4");
arrayList.Add("5");
arrayList.Remove("2");
Console.WriteLine("TOtal count: "+arrayList.Count);
foreach (string i in arrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
OUTPUT:
Monday, 24 February 2025
Web API Vs REST API
| Web API type | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| REST | Follows REST architecture | RESTful |
| SOAP | Utilizes XML, strict standards | Non-RESTful |
| GraphQL | Flexible query language | Non-RESTful |
|
Web
API |
REST
API |
|
|
What
they are |
Web
APIs encompass any API using HTTP or HTTPS. All REST APIs are Web APIs, but
not all Web APIs are RESTful. |
REST
APIs are Web APIs that follow specific architectural principles like
statelessness and client-server architecture. |
|
State |
Technically,
they can be stateless or stateful. |
Statelessness
implies that between sessions of API invocation, the server that hosts the
program doesn’t need to ‘remember’ or hold any information between sessions
to perform the appropriate action. |
|
When to
choose |
Non-RESTful
Web APIs are used for stateful operations, ACID-compliant transactions with a
web server, and working with legacy systems. |
Statelessness
is the main consideration when choosing RESTful APIs over non-RESTful APIs. |
|
Common
use case |
Many
legacy systems, especially those that communicate with systems such as
hardware or IoT devices, also use non-REST-based APIs. |
RESTful
APIs are often used in web services that require standardized communication
and interoperability between different systems. |
Sort the Array without inbuild function
Sorting by ascending order
int[] Arrayorder = {3,7,4,1,2,9,8 };
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < Arrayorder.Length-1; i++)
{
for (int j = i+1; j < Arrayorder.Length; j++)
{
if (Arrayorder[i] > Arrayorder[j])
{
temp = Arrayorder[i];
Arrayorder[i] = Arrayorder[j];
Arrayorder[j] = temp;
}
}
}
foreach (int i in Arrayorder)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Output:
Sorting by Descending order
int[] Arrayorder = {3,7,4,1,2,9,8 };
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < Arrayorder.Length-1; i++)
{
for (int j = i+1; j < Arrayorder.Length; j++)
{
if (Arrayorder[i] < Arrayorder[j])
{
temp = Arrayorder[i];
Arrayorder[i] = Arrayorder[j];
Arrayorder[j] = temp;
}
}
}
foreach (int i in Arrayorder)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Output:
Saturday, 22 February 2025
Delegates SingleCast & MultiCast
In C#, there are two kinds of Delegates. These are:
SingleCast Delegate: A single function or method is referred to as a delegate.
// Using of Delegates
using System;
class Geeks
{
// Declaring the delegates
// Here return type and parameter type should
// be same as the return type and parameter type
// of the two methods
// "addnum" and "subnum" are two delegate names
public delegate void addnum(int a, int b);
public delegate void subnum(int a, int b);
public void sum(int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine("(100 + 40) = {0}", a + b);
}
public void subtract(int a, int b)
{
Console.WriteLine("(100 - 60) = {0}", a - b);
}
// Main Method
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// creating object "obj" of class "Geeks"
Geeks obj = new Geeks();
// creating object of delegate, name as "del_obj1"
// for method "sum" and "del_obj2" for method "subtract" &
// pass the parameter as the two methods by class object "obj"
// instantiating the delegates
addnum del_obj1 = new addnum(obj.sum);
subnum del_obj2 = new subnum(obj.subtract);
// pass the values to the methods by delegate object
del_obj1(100, 40);
del_obj2(100, 60);
// These can be written as using
// "Invoke" method
// del_obj1.Invoke(100, 40);
// del_obj2.Invoke(100, 60);
}
}
MultiCast Delegate: Delegate refers to the delegation of multiple functions or methods.
// C# program to illustrate the
// Multicasting of Delegates
using System;
class rectangle {
// declaring delegate
public delegate void rectDelegate(double height,
double width);
// "area" method
public void area(double height, double width)
{
Console.WriteLine("Area is: {0}", (width * height));
}
// "perimeter" method
public void perimeter(double height, double width)
{
Console.WriteLine("Perimeter is: {0} ", 2 * (width + height));
}
// Main Method
public static void Main(String []args)
{
// creating object of class
// "rectangle", named as "rect"
rectangle rect = new rectangle();
// these two lines are normal calling
// of that two methods
// rect.area(6.3, 4.2);
// rect.perimeter(6.3, 4.2);
// creating delegate object, name as "rectdele"
// and pass the method as parameter by
// class object "rect"
rectDelegate rectdele = new rectDelegate(rect.area);
// also can be written as
// rectDelegate rectdele = rect.area;
// call 2nd method "perimeter"
// Multicasting
rectdele += rect.perimeter;
// pass the values in two method
// by using "Invoke" method
rectdele.Invoke(6.3, 4.2);
Console.WriteLine();
// call the methods with
// different values
rectdele.Invoke(16.3, 10.3);
}
}